-

CLASSIC Clinical Trial: A Methods Study in Unexplained Back Pain
Kathryn Bacik
Axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine including the sacroiliac (SI) joint located at the base of the spine. Over a lifetime, the AxSpA can lead to the fusion of the vertebrae and crippling effects on quality of life. This condition is
subdivided into two forms: ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and non- radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA). While AS is usually
diagnosed using X-ray images that show irreversible bone damage, nr- AxSpA is more difficult to diagnose. In both cases, early detection of
disease will best prevent disease progression and preserve quality of life. An additional form of imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has been valuable in developing more effective AxSpA classification criteria by allowing earlier identification of inflammation within the spine. However, the classification criteria remain under scrutiny due to the lack of specificity in biological markers and physical examinations. The Classification of Axial Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (CLASSIC) study aims to validate the performance of the current classification criteria in a prospective cohort of patients presenting to rheumatologists with low back pain. The study achieves these goals by assessing individual subjects in a step-wise manner that blinds the site primary investigator (PI) to the subject’s information.
-

Changes in Health Behaviors By Gender During a Global Pandemic
Anthony Costarella
As we emerge from Covid-19 pandemic, many people struggle to return to normal, leading us to ask what changes have occurred as a result of the virus and social distancing. We have observed 471 million people suffer with Covid-19, lost 6.08 million lives to the virus, and learned how the virus works as well as how to fight it, yet very little is known about the impact of the virus and its countermeasures on our health habits. PURPOSE: To examine the effect of gender on changes in health behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS: Eight hundred and sixty-six subjects (70.8% female; age= 45±3.4) were surveyed with 129 questions regarding their health behaviors either 1) prior to the pandemic, 2) after the pandemic (current), 3) or the changes in these behaviors they have perceived. The questionnaire utilized a dual set of questions regarding behaviors prior to the pandemic and currently which examined dietary structure, physical activity (using questions from the global physical activity questionnaire (GPAQ), and mental health. For the remaining questions regarding perceived changes, scales were used to indicate the degree of change and whether the behaviors improved or not. The data was analyzed using SPSS 20.0. When analyzing data, first calculated a change score for the pre-pandemic and post-pandemic reported behaviors. These change scores were then used to run independent sample t-tests to identify the differences in changes between males and females, described by means with the accompanying standard deviations. RESULTS: Analysis of the data found that overall, individuals struggled with increased stress, consuming the proper amounts of healthy foods observed (i.e. fruits and vegetables), and with maintaining physical activity levels. When male and female responses were compared, several significant trends emerged. Firstly, females reported a higher increase in anxiety and depression. Secondly, there was little difference found between the changes in nutritional habits and physical activity of men and women. Finally, while observing the data, another trend demonstrated that individuals with children and college students also reported significant increases in stress and a difficulty to maintain nutritional and exercise habits. CONCLUSION: From these findings, it can be concluded that the Covid-19 Pandemic has caused a deficit in health behaviors across the board. It can also be concluded that as a society, we must do more to meet the needs of females, parents, and college students, especially during such a crisis, to help facilitate the maintenance of these behaviors and ensure overall quality of life is an equal opportunity. Further research should explore the identified trends found in parents, college students, and females, as well as underrepresented populations to determine how their needs are not being met, or why they were more likely to suffer as a result of the pandemic.
-

The Evolution of Women in Business During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond
Carleen Ellerbruch
I conducted a survey on the impact of COVID-19 on female professionals in their respective business industries. Respondents to the survey answered a multitude of different questions relating to the impact of COVID-19 on their professional work or their experience in business as a woman.
Any topic covering the pandemic is very new and has very little research or data to support it. The role of women in business continues to evolve and the pandemic is a major factor in its evolution. This survey allows us to gain insight into what will retain women longer, what new challenges needs to be overcome, and what features of the current work environment need to remain in the industry long term.
I am a future woman in business pursuing a career in public accounting after graduation. These are hot topics that will impact anyone in the business world for years to come and especially new graduates.
-
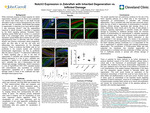
Notch3 Expression in Zebrafish with Inherited Degeneration vs. Inflicted Damage
Meghan Graeca
While mammals possess a limited capacity for retinal regeneration, teleosts such as Danio rerio (zebrafish) can recover from retinal injury or cell death through stimulation of glia to induce reprogramming into neural stem-like cells.
1 In zebrafish, retinal Müller glia engage in regeneration in response to an injury-derived signal. It was previously shown2,3 that the regenerative response to retinal damage in zebrafish is regulated by the Notch signaling pathway. Persistent Notch signaling causes Müller glia to remain in a quiescent state in the undamaged retina, and Notch signaling repression causes Müller glia to reenter the cell cycle3 , reprogramming them to stem-like cells that undergo division and produce multi-potent retinal progenitors, which are then able to exit the cell cycle and differentiate into replacements for the damaged neurons. There is evidence that Müller cells do not proliferate in the mutants studied with inherited photoreceptor degeneration, but they do proliferate after the retina is injured. To determine if differences in Notch signaling play a role in the lack of regeneration in zebrafish with inherited degeneration, Notch3 expression in a line of eys-/- zebrafish was quantified in relation to an unaffected heterozygous eys+/- zebrafish line, and a heterozygous line with inflicted light damage. Additionally, Notch3 expression in a line of Tg(XOPS:ntr-YFP) YFP+ zebrafish treated with metronidazole was quantified to compare regeneration capabilities of a chemical ablation damage model to those of the unaffected and light- damaged heterozygrous lines.
-
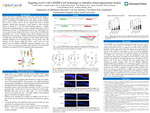
Targeting notch3 with CRISPR-Cas9 technology in zebrafish retinal degeneration models
Emily Januck
Teleost fish such as zebrafish (Danio rerio) have shown the ability to regenerate damaged photoreceptors due to the robust activity of Müller glia [1]. Interestingly, the Müller glia in retinal disease model zebrafish such as bbs2, cep290, and eys do not respond like those in normal zebrafish, making these genotypes a good model to study treatment options in humans [2, 3, 4]. The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling pathway in many organisms that plays a role in determining cell fates in developmental processes [5]. Specifically, the notch3 gene has been studied and shown to have effects on Müller glia proliferation [6,7]. In the zebrafish retina, Notch signaling has been determined to be necessary to inhibit the differentiation and proliferation of Müller glia cells [6]. What is unknown is how retinal disease model zebrafish respond to Notch signaling targets. In the current study, the embryos of each disease model line (bbs2, cep290, and eys) were injected with two different CRISPRs separately, targeting exon 2 and exon 4 of the notch3 gene, and retinal tissue sections of 4–6-month-old zebrafish were stained for PCNA to quantify retinal regeneration.
-

Examining the Optical Properties of Monosodium Urate for the Detection of Gout Using a Magneto-Optical Device (MOD)
Victoria Marino
The purpose of this research was to quantify the magnetooptical properties of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals that would allow for an easy diagnosis using a magneto-optical device (MOD). Characterization of these magnetic and optical properties was achieved by measuring the transmitted light intensity of a laser shining through a sample of monosodium urate with or without an applied (static) magnetic field. Using our theoretical model under the simplifying assumption that absorption is dominant, we determined that the extinction cross-section is σ𝑥 = 0.0127 cm3 /μg and we determined σ𝑧 using two different relationships which gave two distinctly different values. Due to this 78.8% difference in our calculations of σ𝑧 , we determined that the extinction cross section for MSU crystals relies on both scattering and absorption interactions.
-
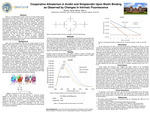
Cooperative Allosterism in Avidin and Streptavidin Upon Biotin Binding as Observed by Changes in Intrinsic Fluorescence
Alycia Murphy
Avidin is a homotetrameric protein known for its high binding affinity and specificity for biotin which gives it great functionality in many biotech applications. Prior research on the bacterial analog, streptavidin found cooperative allosterism exhibited in the binding process. This research was aimed at investigating whether this same cooperative allosterism accompanies the binding of biotin to avidin. This work measured intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence as biotin was titrated into avidin. A blueshift in the wavelength of maximum fluorescence as well as quenching of the overall fluorescence intensity, similar to the streptavidin was observed. The saturation point for 335 nm emission (tryptophans in more hydrophobic environments) was lower than the 4:1 stoichiometric ratio exhibited by the 350 nm emission (tryptophans in more hydrophilic environments). This suggest biotin binding to avidin exemplifies cooperative allosterism similar to that of streptavidin. Additional fluorescence based parameters were also examined and will be described relative to those for streptavidin as well.
-

How Study and Test Formats Impact Foreign Language Vocabulary Learning: Pictures vs. Words
Marie Pinzone
Background: The Revised Hierarchical Model suggests FL vocabulary acquisition is mediated and enhanced by native language vocabulary knowledge (Kroll & Stewart, 1994). The PSE, based on Paivio’s dual coding theory, holds that pictures are remembered better than words due to being encoded by both verbal and pictorial codes (Paivio & Csapo, 1973). Mixed evidence exists regarding whether the PSE obtains in FL vocabulary learning (Carpenter & Olson, 2012). Hockley (2008) found that the PSE for associative recognition occurs even when picture pairings are presented as words at test. Current Study: The present study seeks to replicate and extend the investigation of the PSE for FL learning. Experiment 1 manipulated study modality only (picture vs. word). Experiment 2 manipulated both study (picture vs. word) and test (picture vs. word) modality.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

